Tuesday, June 22, 2010
Friday, February 19, 2010
LAND POLLUTION AND THEIR CONTROL




Organic and inorganic matter disposed on the lead as waste due to various activities are classifiedinto Degradable and Non-degradable pollutants.
Pollutants like domestic sewage which can be recycled by waste treatment mechanism comes under degradable pollutants. Garbage from houses comes under this category. There are limits tothe total amount of organic matter that can be decomposed in a given place, beyond which it becomes a breeding place for pathogens.
NON-DEGRADABLE POLLUTANTS
Aliminium cans, PVC, articles, mercuric chloride, ceramics, pesticides, etc. are non-degradable pollutants. In these substances, the degrading process is very slow in the natural environment. There is no waste treatment mechanism available for these pollutants.
The detergents used for washing purposes whendischarged into the soil affect the soil fertility.
CONTROL OFLAND POLLUTION
Proper treatment of bio-degradable substances like sewage should be followed. Usage of non-biodegradable substances sghould be minimized
Saturday, February 13, 2010
WATER POLLUTION




CAUSES OF WATER POLLUTION
Major water pollutants are solid and liquid wastes dumped into water sources. Sewage, chemicals, biproducts of refineries, wastes from tanneries from major effluents from factories which cause water pollution.
Water pollution affects biotic and abiotic factors of aquatic eco-system. Polluted water contains disease producing bacteria and viruses which may cause disease like cholera, jaundice, dysentery, poliomyelites, typhoid, etc.
At times rich supply of nutrients from the nearby fields may go to into the water source and land and result in sudden growth of algae which" Algal bloom ". This also causes pollution of water
CONTROL OF WATER POLLUTION
Proper drainage facilities are to be given for human and animals wastes of water.Proper filtering mechanism should be followed to avoid the effectsof water pollution. Industrial effluents should be treated before releasing them into water source.
Wednesday, February 10, 2010
AIR POLLUTION




BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF AIRPOLLUTION
1.Smoke particles block the surface of the plants, and hence photosynthesis gets affected.
2.Carbon dioxide,nitrogen dioxide and sulphurdioxide, when mixed with water vapour comes down as Acid rain which has a detrimental effect on plants and animals.
3.Number of respirtory diseases such as bronchitis and asthma are aggravated by smoke filled air.
4.Unburnt hydrocarbons are cancer causing.
5.Nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide irritate eyes, nose and lungs.
CONTROL OF AIR POLLUTION
1.Planting trees and maintaining parks and gardens may reduce air pollution and give good air.
2.Adulteration of petrols should be controlled.
3.Less use of coal and oil for running factories.
4.Nuclear tests have to be followed under controlled conditions.
5.Lead free petrol should be used in automobiles.
6.Strict vigil against leakage of poisonous gases in the gas factories
Sunday, February 7, 2010
ECO BALANCE


Ecology is the study of relationship between an organism and the environment.In an environment, plants, animals, and microbes lead an interconnected existence. In turn the organisms are interlinked with abiotic factors of the environment like light, rain,temperature, soil, etc.
When plants and animals are connected with each other due to interdependence of food requirement it is called a food chain. The passing of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level is called a food chain can be interrelated to form a food web.
Eco-balance is the maintance of natural interrelationships between biotic and abiotic factors. By these natural interrelationship an ecological balance is maintained in nature. When this link is broken at one point the balance gets affected
EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING

1.Due to the warming of oceans, there will be an increase in sea level.Melting of glacieries may also influence the above factors. Such rise will submerge many parts of countries.
2.Growing seasons may show distinct changes.
3.Storms and Hurricanes may be more frequent and intense.
4.Some regions of the world will become drier.
5.Greater humidity may increase rainfall, casuing floods
Tuesday, January 26, 2010
GLOBAL WARMING

Global warming, refers to an average increase in the earth's temperature, which in turn causes changes in the climate of the environment. During the past 4.65 billions years of its history, earth has shown a continuous increase in its temperature. The average temperature of earth is about 59 degree F(15 degree C).By the year 2100, it is believed that the rise would be between 2.5 and 10.4 degree F. This increase may cause many changes in the earth's environment.
The trapping of solar energy by certaingases which lead to increase in earth's temperature is called "grenhouse effect"leading to global warming.
Normally all the living organisms depend on this green house effect. Otherwise the earth would become cooled down, and ice would cover from pole to pole. This does not happen because the earth is kept warm by these green house effect,caused by burning of fuels, and deforestation may cause harmful increase in earth's temperature.
Greenhouse gases are carbondioxide,methane,nitrous oxide,chlorofluocarbon etc.The following is the list of sources of these greenhouse gases.
Monday, January 18, 2010
ozone layer

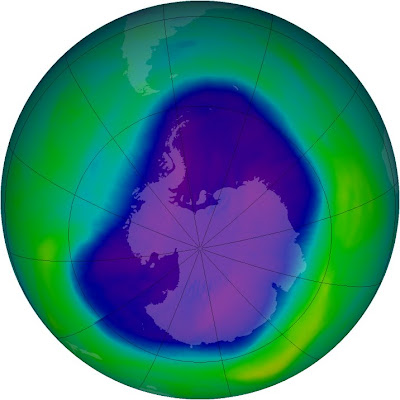
The ozone layer prevents most ultraviolet (UV) and other high-energy radiation from penetrating to the earth's surface but does allow through sufficient ultraviolet rays to support the activation of vitamin D in humans.
The full radiation, if unhindered by this filtering effect, would destroy animal tissue. Higher levels of radiation resulting from the depletion of the ozone layer have been linked with increases in skin cancers and cataracts and have been implicated in the decline of certain amphibian species
Minimum ozone levels in the Antarctic decreased steadily throughout the 1990s, and less dramatic decreases have been found above other areas of the world. In 2000 (and again in 2003 and 2006) the hole reached a record size, extending over more than 10.5 million sq mi (27 million sq km), an area greater than that of North America. In 1987 an international agreement, the Montreal Protocol, was reached on reducing the production of ozone-depleting compounds.
Revisions in 1992 called for an end to the production of the worst of such compounds by 1996, and CFC emissions dropped dramatically by 1993. Recovery of the ozone layer, however, is expected to take 50 to 100 years. Damage to the ozone layer can also be caused by sulfuric acid droplets produced by volcanic eruptions.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
